Summary: in this tutorial, you’ll learn about the Promise.allSettled() method to compose promises.
Introduction to the Promise.allSettled() method
ES2020 introduced the Promise.allSettled() method that accepts a list of Promises and returns a new promise that resolves after all the input promises have settled, either resolved or rejected.
The following shows the syntax of the Promise.allSettled() method:
Promise.allSettled(iterable);Code language: JavaScript (javascript)The iterable contains the promises. The Promise.allSettled() returns a pending promise that will be asynchronously fulfilled once every input promise has settled.
The Promise.allSettled() method returns a promise that resolves to an array of objects that each describes the result of the input promise.
Each object has two properties: status and value (or reason).
- The
statuscan be eitherfulfilledorrejected. - The
valueif case the promise is fulfilled orreason) if the promise is rejected.
The following diagram illustrates how the Promise.allSettled() method works:
In this diagram:
- The
promise1rejects to theerroratt1. - The
promise2resolves to avalueatt2. - The
Promise.allSettled()method resolves to an array containing objects that describe the statuses and outcomes of thepromise1andpromise2.
JavaScript Promise.allSettled() example
The following example uses the Promise.allSettled() to wait for all the input promises to settle:
const p1 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('The first promise has resolved');
resolve(10);
}, 1 * 1000);
});
const p2 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('The second promise has rejected');
reject(20);
}, 2 * 1000);
});
Promise.allSettled([p1, p2])
.then((result) => {
console.log(result);
});
Code language: JavaScript (javascript)Output:
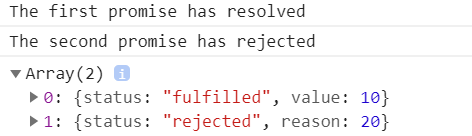
How it works:
- The first promise
p1resolves to the value10after one second - The second promise
p2rejects for a reason with a value20after two seconds. - The
Promise.allSettled()returns a promise that resolves to theresultarray that has two elements. The first element is an object resolved by thep1promise and the second one is another object which is rejected by thep2promise.
Summary
- The
Promise.allSettled()method accepts an iterable of promises and returns a new promise that resolves when every input promise has settled with an array of objects that describes the result of each promise in the iterable object.