Summary: in this tutorial, you’ll learn how to implement the JavaScript infinite scroll feature.
What you’re going to build
The following picture illustrates the web application that you’re going to build:
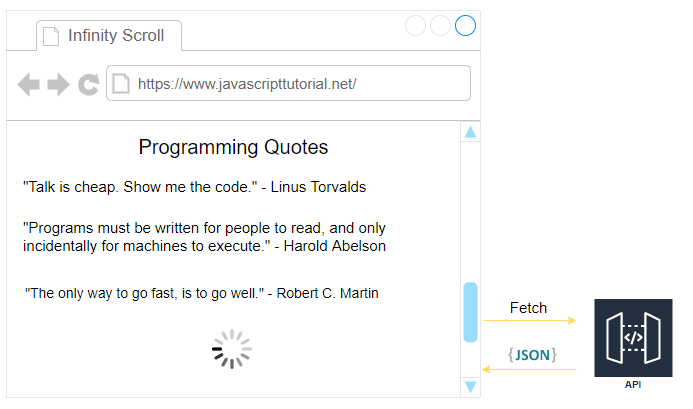
The page will display a list of quotes that come from an API. By default, it shows 10 quotes.
If you scroll down to the bottom of the page, the web application will display a loading indicator. In addition, it’ll call the API to fetch more quotes and append them to the current list.
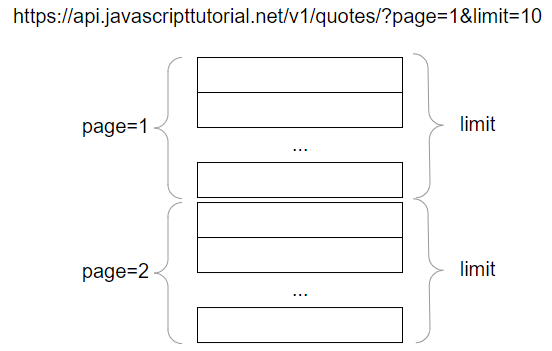
The URL of the API that you’re going to use is as follows:
https://api.javascripttutorial.net/v1/quotes/?page=1&limit=10Code language: JavaScript (javascript)The API accepts two query strings: page and limit. These query strings allow you to paginate the quotes from the server.
The quotes are divided into the pages determined by the page query string. And each page has a number of quotes specified by the limit parameter.
Click here to see the final web application that uses the JavaScript infinite scroll feature.
Create a project structure
First, create a new folder called infinite-scroll. Inside that folder, create two subfolders css and js.
Second, create the style.css in the css folder and app.js in the js folder.
Third, create a new HTML file index.html in the infinite-scroll folder.
The final project folder structure will look like this:
Add code to the index.html file
Open the index.html and add the following code to it:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>JavaScript Infinite Scroll - Quotes</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/style.css">
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<h1>Programming Quotes</h1>
<div class="quotes">
</div>
<div class="loader">
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
</div>
</div>
<script src="js/app.js"></script>
</body>
</html>Code language: HTML, XML (xml)In the index.html file, place the style.css in the head section and app.js in the body section.
The body section has a div with the class name container. The container element has four child elements:
- A heading one (h1) that shows the page heading.
- A
divwith the classquotesthat will be the parent element of all the quotes. - A loader that displays the loading indicator. By default, the loading indicator is invisible.
Making the app.js
The following uses the querySelector() to select the div with class quotes and the loader .
const quotesEl = document.querySelector('.quotes');
const loader = document.querySelector('.loader');Code language: JavaScript (javascript)The getQuotes() function
The following getQuotes() function calls the API and return the quotes:
const getQuotes = async (page, limit) => {
const API_URL = `https://api.javascripttutorial.net/v1/quotes/?page=${page}&limit=${limit}`;
const response = await fetch(API_URL);
// handle 404
if (!response.ok) {
throw new Error(`An error occurred: ${response.status}`);
}
return await response.json();
}Code language: JavaScript (javascript)The getQuotes() function accepts two arguments: page and limit. It uses the Fetch API to fetch data from the API.
Since the fetch() returns a promise, you can use the await syntax to get the response. And you call the json() method of the response object to get the json data.
The getQuotes() returns a promise that will resolve to the JSON data.
Since the getQuotes() function use the await keyword, it has to be an async function.
The showQuotes() function
The following defines the showQuotes() function that generates the <blockquote> elements from the quotes array and appends them to the quotes element:
// show the quotes
const showQuotes = (quotes) => {
quotes.forEach(quote => {
const quoteEl = document.createElement('blockquote');
quoteEl.classList.add('quote');
quoteEl.innerHTML = `
<span>${quote.id})</span>
${quote.quote}
<footer>${quote.author}</footer>
`;
quotesEl.appendChild(quoteEl);
});
};Code language: JavaScript (javascript)How it works:
The showQuotes() uses the forEach() method to iterate over the quotes array.
For each quote object, it creates the <blockquote> element with the quote class:
<blockquote class="quote">
</blockquote>Code language: HTML, XML (xml)And it generates the HTML representation of a quote object using the template literal syntax. It adds the HTML to the <blockquote> element.
The following shows an example of the generated <blockquote> element:
<blockquote class="quote">
<span>1)</span>
Talk is cheap. Show me the code.
<footer>Linus Torvalds</footer>
</blockquote>Code language: HTML, XML (xml)At the end of each iteration, the function appends the <blockquote> element to the child elements of the quotesEl element by using the appendChild() method.
Show/hide loading indicator functions
The following defines two functions that show and hide the loading indicator element:
const hideLoader = () => {
loader.classList.remove('show');
};
const showLoader = () => {
loader.classList.add('show');
};Code language: JavaScript (javascript)The loading indicator has the opacity 0, which is invisible by default. The .show class sets the opacity of the loading indicator to 1 that will make it visible.
To hide the loading indicator, you remove the show class from the loading indicator element. Similarly, to show the loading indicator, you add the show class to its class list.
Define control variables
The following declares the currentPage variable and initialize it to one:
let currentPage = 1;Code language: JavaScript (javascript) When you scroll down to the end of the page, the application will make an API request to get the next quotes. Before doing so, you need to increase the currentPage variable by one.
To specify the number of quotes that you want to fetch at a time, you can use a constant like this:
const limit = 10;Code language: JavaScript (javascript)The following total variable stores the total of quotes returned from the API:
let total = 0;Code language: JavaScript (javascript)The hasMoreQuotes() function
The following hasMoreQuotes() function returns true if:
- It’s the first fetch (
total === 0) - Or there are more quotes to fetch from the API (
startIndex<total)
const hasMoreQuotes = (page, limit, total) => {
const startIndex = (page - 1) * limit + 1;
return total === 0 || startIndex < total;
};Code language: JavaScript (javascript)The loadQuotes() function
The following defines a function that performs four actions:
- Show the loading indicator.
- Get the quotes from the API by calling the
getQuotes()function if there are more quotes to fetch. - Show the quotes on the page.
- Hide the loading indicator.
// load quotes
const loadQuotes = async (page, limit) => {
// show the loader
showLoader();
try {
// if having more quotes to fetch
if (hasMoreQuotes(page, limit, total)) {
// call the API to get quotes
const response = await getQuotes(page, limit);
// show quotes
showQuotes(response.data);
// update the total
total = response.total;
}
} catch (error) {
console.log(error.message);
} finally {
hideLoader();
}
};Code language: JavaScript (javascript)If the getQuotes() function executes very fast, you won’t see the loading indicator.
To make sure that the loading indicator always showing, you can use the setTimeout() function:
// load quotes
const loadQuotes = async (page, limit) => {
// show the loader
showLoader();
// 0.5 second later
setTimeout(async () => {
try {
// if having more quotes to fetch
if (hasMoreQuotes(page, limit, total)) {
// call the API to get quotes
const response = await getQuotes(page, limit);
// show quotes
showQuotes(response.data);
// update the total
total = response.total;
}
} catch (error) {
console.log(error.message);
} finally {
hideLoader();
}
}, 500);
};Code language: JavaScript (javascript)By adding the setTimeout() function, the loading indicator will show for at least a half-second. And you can tweak the delay by changing the second argument of the setTimeout() function.
Attach the scroll event
To load more quotes when users scroll to the bottom of the page, you need to attach a scroll event handler.
The scroll event handler will call the loadQuotes() function if the following conditions are met:
- First, the scroll position is at the bottom of the page.
- Second, there are more quotes to fetch.
The scroll event handler will also increase the currentPage variable before loading the next quotes.
window.addEventListener('scroll', () => {
const {
scrollTop,
scrollHeight,
clientHeight
} = document.documentElement;
if (scrollTop + clientHeight >= scrollHeight - 5 &&
hasMoreQuotes(currentPage, limit, total)) {
currentPage++;
loadQuotes(currentPage, limit);
}
}, {
passive: true
});Code language: JavaScript (javascript)Initialize the page
When the page loads for the first time, you need to call the loadQuotes() function to load the first batch of quotes:
loadQuotes(currentPage, limit);Wrap app.js code in an IIFE
To avoid the conflict of variables and functions that you have defined, you can wrap the whole code in the app.js file in an IIFE.
The final app.js will look like this:
(function () {
const quotesEl = document.querySelector('.quotes');
const loaderEl = document.querySelector('.loader');
// get the quotes from API
const getQuotes = async (page, limit) => {
const API_URL = `https://api.javascripttutorial.net/v1/quotes/?page=${page}&limit=${limit}`;
const response = await fetch(API_URL);
// handle 404
if (!response.ok) {
throw new Error(`An error occurred: ${response.status}`);
}
return await response.json();
}
// show the quotes
const showQuotes = (quotes) => {
quotes.forEach(quote => {
const quoteEl = document.createElement('blockquote');
quoteEl.classList.add('quote');
quoteEl.innerHTML = `
<span>${quote.id})</span>
${quote.quote}
<footer>${quote.author}</footer>
`;
quotesEl.appendChild(quoteEl);
});
};
const hideLoader = () => {
loaderEl.classList.remove('show');
};
const showLoader = () => {
loaderEl.classList.add('show');
};
const hasMoreQuotes = (page, limit, total) => {
const startIndex = (page - 1) * limit + 1;
return total === 0 || startIndex < total;
};
// load quotes
const loadQuotes = async (page, limit) => {
// show the loader
showLoader();
// 0.5 second later
setTimeout(async () => {
try {
// if having more quotes to fetch
if (hasMoreQuotes(page, limit, total)) {
// call the API to get quotes
const response = await getQuotes(page, limit);
// show quotes
showQuotes(response.data);
// update the total
total = response.total;
}
} catch (error) {
console.log(error.message);
} finally {
hideLoader();
}
}, 500);
};
// control variables
let currentPage = 1;
const limit = 10;
let total = 0;
window.addEventListener('scroll', () => {
const {
scrollTop,
scrollHeight,
clientHeight
} = document.documentElement;
if (scrollTop + clientHeight >= scrollHeight - 5 &&
hasMoreQuotes(currentPage, limit, total)) {
currentPage++;
loadQuotes(currentPage, limit);
}
}, {
passive: true
});
// initialize
loadQuotes(currentPage, limit);
})();Code language: JavaScript (javascript)Here is the final version of the web application.